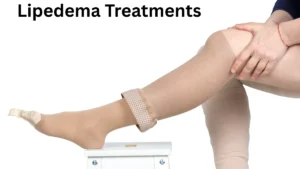
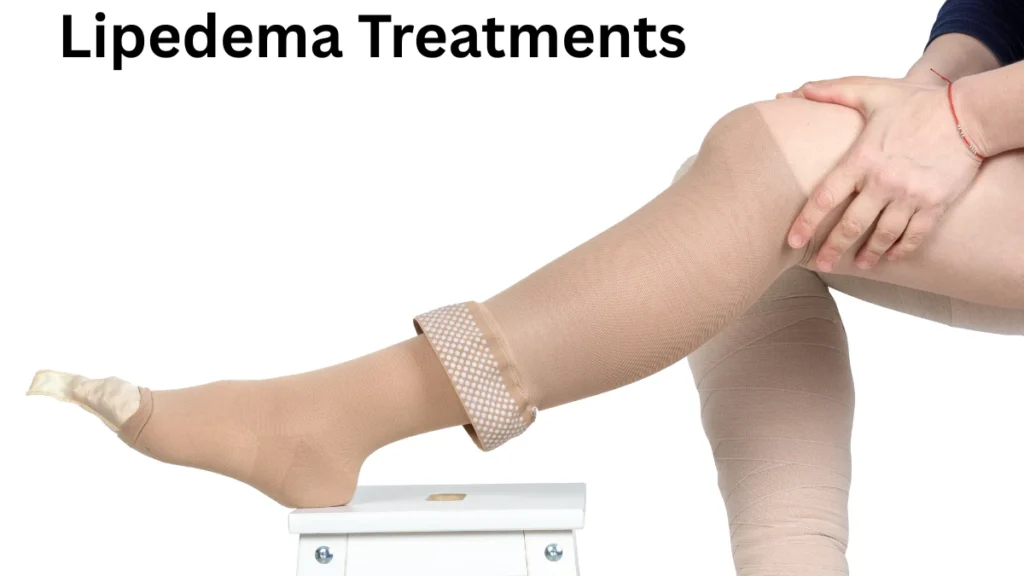
Lipedema Treatments: Lipedema is a chronic, progressive condition that causes abnormal fat accumulation—mainly in the hips, thighs, and legs—leading to pain, swelling, and reduced mobility. Often misdiagnosed as obesity or lymphedema, lipedema primarily affects women and requires accurate diagnosis and effective management. While there is no permanent cure, a variety of treatments are available to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Lipedema Treatments
| Treatment Type | Method/Approach | Purpose/Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Compression Therapy | Compression stockings, bandages | Reduces swelling, improves blood and lymph flow |
| Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD) | Gentle lymphatic massage technique | Stimulates lymph drainage, reduces fluid buildup |
| Exercise | Low-impact (swimming, cycling, walking) | Enhances mobility, lymphatic circulation, reduces stiffness |
| Dietary Modifications | Anti-inflammatory diet, weight management | Helps manage symptoms, reduces inflammation |
| Skin Care | Moisturizers, gentle skin protection | Prevents dryness, irritation, and infection |
| Supplements/Medications | Diosmin, resveratrol, selenium (with doctor consultation) | May reduce inflammation and support vein/lymph function |
| Liposuction | Tumescent liposuction (surgical removal of fat) | Removes abnormal fat, reduces pain and improves quality of life |
| Skin Excision | Surgical removal of excess skin | Improves hygiene and comfort in advanced cases |
| Lymphatic Surgery | Bypass or lymph node transfer | Improves lymphatic drainage in rare cases |
| Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT) | Combined MLD, compression, exercise, skin care | Comprehensive non-surgical approach for symptom control |
| Pressotherapy | Air pressure therapy to stimulate lymphatic drainage | Reduces swelling and enhances comfort |
| Bariatric Surgery | Weight-loss surgery (in obesity-related cases) | Reduces overall leg volume and stress on lymphatic system |
| Emotional Support | Counseling, support groups, mental health therapy | Helps cope with emotional and psychological impact of lipedema |
What Is Lipedema?
Lipedema is a fat disorder that causes bilateral, symmetrical fat deposits on the legs, buttocks, and sometimes arms. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent swelling in the legs or arms
- Painful, tender fat that doesn’t respond to diet or exercise
- Easy bruising
- Feeling of heaviness in the limbs
- Emotional stress or depression due to body changes
Lipedema can progress if untreated, making early recognition and intervention crucial.
Read more: Top 10 Effective Constipation Treatments: Causes, Remedies & When to See a Doctor
Top 10 Effective Treatments for Lipedema
1. Compression Therapy
Wearing compression garments (stockings or bandages) supports lymphatic flow, reduces swelling, and relieves heaviness in the limbs. It also helps prevent the buildup of fluid that worsens symptoms.
2. Manual Lymphatic Drainage (MLD)
MLD is a specialized, light-touch massage technique that promotes lymphatic circulation. This therapy is often used in conjunction with compression to manage fluid retention and ease pain.
3. Low-Impact Exercise
Gentle exercises such as swimming, walking, cycling, and aqua aerobics improve mobility and lymph flow without stressing the joints. Regular movement helps prevent stiffness and enhances overall function.
4. Anti-Inflammatory Diet
While diet alone can’t cure lipedema, reducing inflammation through nutrition can improve symptoms. Focus on:
- Vegetables and leafy greens
- Omega-3 fatty acids (from fish, chia seeds, flaxseed)
- Lean proteins
- Avoiding sugar, processed foods, and refined carbs
5. Skin Care
Skin affected by lipedema is prone to dryness, irritation, and infections. Daily moisturizing and gentle hygiene can protect the skin, especially when using compression garments.
6. Medications and Supplements
Though not a replacement for physical treatment, certain supplements may support symptom control:
- Diosmin – boosts vein tone and lymphatic flow
- Resveratrol – an antioxidant that reduces inflammation
- Selenium – improves immune response
Always consult a healthcare provider before adding new supplements to your routine.
7. Liposuction (Tumescent Liposuction)
Liposuction is one of the few surgical treatments shown to provide long-term relief. Tumescent liposuction specifically targets abnormal fat and preserves lymphatic function, improving pain, mobility, and quality of life.
8. Skin Excision Surgery
In advanced stages, sagging or stretched skin may interfere with movement or hygiene. Excision surgery can remove this excess skin and restore comfort.
9. Lymphatic Surgery
In rare cases, patients may undergo lymphatic bypass or lymph node transfer to improve drainage. This is usually recommended if lipedema overlaps with lymphedema.
10. Complete Decongestive Therapy (CDT)
CDT is a combination approach that includes MLD, compression, exercise, and skin care. It is considered the gold standard in non-surgical treatment for lipedema and helps slow the progression of the disease.
Read more: Epidural Injection Price in UAE: What Expecting Mothers Should Know in 2025
FAQs
FAQs About Lipedema Treatment
1. What is the best treatment for lipedema?
The most effective treatment varies depending on the stage and severity of lipedema. Conservative treatments like compression therapy and manual lymphatic drainage are highly recommended. In advanced cases, tumescent liposuction is considered the most effective surgical option.
2. Can lipedema go away with diet and exercise?
No, lipedema fat is resistant to traditional weight loss methods. However, an anti-inflammatory diet and regular low-impact exercise can help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and improve overall health.
3. Is lipedema the same as lymphedema?
No, lipedema and lymphedema are different conditions. Lipedema involves abnormal fat deposits, while lymphedema is caused by lymph fluid buildup. However, in later stages, lipedema can lead to secondary lymphedema (also called lipolymphedema).
4. Who is most likely to develop lipedema?
Lipedema primarily affects women, often starting or worsening during hormonal changes such as puberty, pregnancy, or menopause. It may also have a genetic link, as it tends to run in families.
5. What kind of doctor should I see for lipedema?
A vascular specialist, dermatologist, or a physician who specializes in lymphatic disorders can diagnose and treat lipedema. Look for clinics with experience in treating lymphatic and fat disorders.
6. Is liposuction a permanent cure for lipedema?
Liposuction can provide long-term relief by removing diseased fat, improving mobility, and reducing pain. However, it is not a cure. Ongoing management through lifestyle and compression therapy may still be necessary.
7. How do I know if I have lipedema and not just obesity?
If you have symmetrical fat accumulation in your legs or arms, pain when touched, easy bruising, and no response to dieting, you might have lipedema. Consult a medical professional for an accurate diagnosis.
8. Is lipedema painful?
Yes, lipedema is often painful. Affected areas may feel tender, sore, or heavy. Pain can worsen over time if left untreated.
9. What are the early signs of lipedema?
Early signs include a disproportionate lower body shape, persistent swelling, tenderness, and bruising. These symptoms typically do not improve with weight loss or elevation.
10. Can men have lipedema?
Although rare, lipedema can affect men, especially those with hormonal imbalances or genetic conditions. It is significantly more common in women.