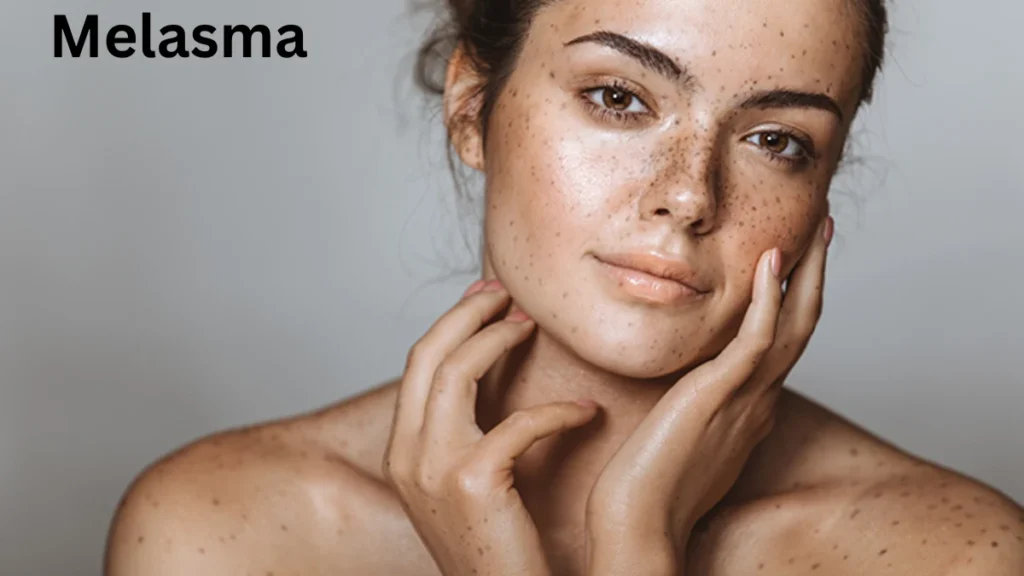
Melasma is a common skin condition that causes dark, brown, or grayish-brown patches, primarily on the face. It most often affects women, especially during pregnancy or when using hormonal birth control, but anyone can develop it. While melasma is harmless medically, it can be distressing cosmetically and affect self-confidence. Understanding what causes melasma, how to recognize it, and the available treatments can help those affected manage the condition effectively.
| Category | Details |
|---|---|
| Condition Name | Melasma |
| Also Known As | Chloasma, Mask of Pregnancy |
| Commonly Affects | Women (especially pregnant women), people with darker skin tones |
| Primary Cause | Sun exposure |
| Other Causes | Hormonal changes, genetics, skin irritation, certain medications |
| Main Symptoms | Dark, brown, or grayish-brown patches on face (cheeks, forehead, upper lip) |
| Types | Epidermal, Dermal, Mixed |
| Diagnosis | Clinical examination, Wood’s lamp, dermoscopy |
| Topical Treatments | Hydroquinone, Tretinoin, Corticosteroids, Azelaic Acid, Kojic Acid |
| Oral Medications | Tranexamic Acid |
| Procedures | Chemical peels, Laser therapy, Microdermabrasion |
| Natural Remedies | Aloe vera, Turmeric, Licorice extract (mild results) |
| Prevention | Sunscreen use, protective clothing, avoid known triggers |
| Is It Harmful? | No, it is not medically harmful, but it may affect self-esteem |
| Is It Curable? | Not permanently, but manageable with consistent treatment and prevention |
| Specialist to Consult | Dermatologist |
What is Melasma?
Melasma is a form of hyperpigmentation, meaning it causes areas of skin to become darker than the surrounding skin. These dark patches typically appear on sun-exposed areas such as the cheeks, forehead, chin, upper lip, and sometimes on the arms or neck. The pigmentation tends to be symmetrical, affecting both sides of the face.

Causes of Melasma
Several factors contribute to the development of melasma:
1. Sun Exposure
The primary trigger of melasma is ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. UV rays stimulate melanocytes, the skin cells that produce melanin, leading to increased pigmentation.
2. Hormonal Changes
Hormonal fluctuations play a significant role in melasma. Pregnant women often experience melasma, called “chloasma” or the “mask of pregnancy.” Birth control pills, hormone replacement therapy, and other hormonal treatments can also trigger melasma.
3. Genetics
Melasma often runs in families. People with darker skin tones, such as those of Latin, Asian, Middle Eastern, or Mediterranean descent, are more prone to developing melasma.
4. Skin Trauma or Irritation
Repeated irritation or inflammation of the skin from cosmetic procedures, harsh skincare products, or even excessive scrubbing may worsen melasma.
5. Other Triggers
Stress, thyroid disorders, and heat exposure may also contribute to or aggravate melasma.
Read more: Top 7 Powerful Benefits of Acupuncture: How It Works, Safety Tips & What to Expect
Symptoms: How to Recognize Melasma
Melasma appears as irregular, well-defined patches of darker pigmentation. The color can range from light brown to grayish brown, and the patches are often symmetrical on both sides of the face. Unlike freckles or age spots, melasma patches are usually larger and more diffuse.
Types of Melasma
Melasma can be classified based on the depth of pigmentation:
- Epidermal Melasma: Involves pigmentation in the upper layers of the skin. These patches tend to be darker and respond better to treatment.
- Dermal Melasma: Affects deeper skin layers, causing a bluish-gray discoloration. This type is more challenging to treat.
- Mixed Melasma: Features characteristics of both epidermal and dermal types.
Diagnosis: When to See a Dermatologist
If you notice persistent dark patches on your face, it’s important to consult a dermatologist. Diagnosis is primarily through visual examination, but dermatologists may use a Wood’s lamp or dermoscopy to assess the depth of pigmentation and rule out other skin conditions.
Treatment Options for Melasma
Although melasma can be stubborn, various treatments can lighten pigmentation and improve skin appearance:
Topical Treatments
- Hydroquinone: A skin-lightening agent often considered the gold standard for melasma treatment.
- Tretinoin: Helps with skin cell turnover and enhances hydroquinone’s effects.
- Corticosteroids: Sometimes combined with other creams to reduce inflammation.
- Azelaic Acid and Kojic Acid: Alternatives that lighten skin pigmentation.
Oral Medications
- Tranexamic Acid: Used in some cases to reduce melasma by inhibiting melanin synthesis.
Procedures
- Chemical Peels: Help exfoliate and remove pigmented skin layers.
- Microdermabrasion: A mechanical exfoliation technique.
- Laser Therapy: Used cautiously, as it may worsen pigmentation if not done properly.
Natural Remedies
Some people try natural ingredients like aloe vera, turmeric, or licorice extract. While they may offer mild benefits, they are generally less effective than medical treatments.
Read more: Plantar Fasciitis Treatment: A Complete Guide to Healing Heel Pain
Prevention and Management
Preventing melasma flare-ups is essential to managing the condition:
- Use Broad-Spectrum Sunscreen: Apply sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher daily, even on cloudy days.
- Wear Protective Clothing: Hats and sunglasses help reduce sun exposure.
- Avoid Known Triggers: Minimize hormonal treatments or skincare products that irritate your skin.
- Maintain a Gentle Skincare Routine: Avoid scrubbing or harsh exfoliation.
Living with Melasma
Melasma is a chronic condition that may recur despite treatment. It can affect emotional well-being, but cosmetic options like makeup can help camouflage patches. Support from a dermatologist and a consistent skincare regimen can greatly improve quality of life.
Read more: Best Insurance Company in UAE Orient Insurance
Conclusion
Melasma is a common but treatable skin condition characterized by brown patches, mainly on the face. Though harmless, it can cause cosmetic concerns. Understanding its causes, recognizing symptoms early, and following a comprehensive treatment and prevention plan can help achieve clearer, more even-toned skin. Always seek professional advice for proper diagnosis and personalized treatment.